1 Introduction
This article provide an introduction to Azure Cosmos DB and its extensive features including data partitioning, global distribution, elastic scaling, latency, throughput and different service level agreements.It describes how you can design your cosmos db with different collections and relationships, You can run queries top of that design and analyse throughput of the query. If its not performing up to the expected level, you can remodel your database until it reaches to an expected level
2 What is Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is a database service that offers variety of data models and data APIsIt supports for key-value storage, document db and graph db
It is a global distributed database service, with a single button click you can replicate your data into different regions, You can scale out your database runs in Azure Cosmos DB service, when the no of users increases and same time you can achieve low response time
Azure Cosmos DB service offers no of service level agreements, which vary with amount of availability of your data and consistency of your data, you can select according to your business requirements
If you want to distribute your data into multiple regions, closer to your users, when you want to scale out your application, when application grows and at the same time you need to achieve low latency, high data availability & consistency, you can go for Azure CosmosDB
3 Why Azure Cosmos DB
Let's see what is the difference between Azure SQL database and Azure Cosmos DB, Both databases are database servicesAzure Cosmos DB supports for document store, Graph DBMS, key value store and column store. SQL databases supports for relational database systems.
Both database services can be replicated to many data centres and achieve high data availability. We can scale out and improve latency in both database services
Azure SQL databases and Azure Cosmos DB both has different level of service agreements.
4 Data Partitioning & Global Distribution
Data in Azure Cosmos DB can be partitioned into different sections. Let's say we have products and product categories, you can define product category as the partition key and split products into different sections, partitions as above picture. If we take East Asia region, products has been locally distributed according to the product category id, (product category A, B & C) products has distributed globally for different regions like East Asia, Central US and West US
You can host copy of your data along with the partitions into another region and make data synchronize with each other
You can configure multiple read/write regions, one region can act as a write region and all the other regions can act as read regions. you can order fail over regions, If East Asia goes down, read from Central US, If East Asia & Central US both goes down, read from West US
In above picture I have hosted cosmos db in East Asia region, since i haven't hosted this cosmos db in multiple regions, read & write location will be East Asia region. Let's see how we can host our database service in multiple regions and how to configure read, write regions
Go to region configuration in Cosmos DB, you can see 'Replicate data globally' screen. click on a region and you can replicate your data into different regions, i have replicated data to Central US & West US regions. You can see write region & read region configuration, I selected East Asia as a write region and Central US & West US as read regions, primary read region is Central US in this scenario. You can order your data read regions as you want.
5 Data Consistency & Availability
What happens to data consistency & availability when you distribute your data within multiple regions, You cant't achieve high level of data availability & consistency in same timeYour application requirements should decide what to do, whether to provide highly available system or to focus on consistency in your data, In a shopping cart application, you may get duplicate items, sometime items you added to the cart may not be there, that's not good for a better user experience, but It's acceptable. When it comes to a mission critical application, your data should be high consistent.
If you partition your data, you have to choose either consistency or availability, If we get a one db instance it's not a problem
You have to decide whether to focus on consistency or availability, but that's not a single binary choice. You can go for a certain amount of consistency with certain amount of availability as per your requirements. In Cosmos DB, you can select level of data consistencies, it can depend on the operations you need to perform
cosmos DB offers 99.9% availability SLA with 5 different consistency levels such as strong to eventual, In strong consistency its not high available, response time will be high, not easy to scale. In eventual consistency level, data not consistent & it shows out of order reads
In a Cosmos DB service, default consistency level is session consistency, session consistency is useful for user centric applications. you can get a consistent view of your data in your region, but you may not see latest data in other regions as soon as you commit your changes, its more user centric
You can change your consistency level programmatically, If you want to read more consistent data in a specific read, you can increase the consistency level and achieve strongly consistent index and data
Go to default consistency in Cosmos DB service, you can see available consistency levels and can select one of them
6 Data Consistency vs Response time
It's not the consistency vs availability you are dealing with, it's with response time.The more you want to have consistent across the nodes, more nodes need to involve with communication, it's going to slow down the response time
You can let your each node work with different actions and sort it later. In that case, you can get high response time even your data is not consistent. Again that's a business decision. Even though your network is up, you can sync up things but don't go and do it, if you want to have high response time
If you build a system that deals with safety and aliveness, you can give more concentrate on data consistency, even though your system has low response time
7 Scale throughput and storage
You can elastically scale out database throughput, measured in seconds or minutesYou can scale out Cosmos DB as per the size requirements of your application
8 Database schema & Index management
In Cosmos DB service, it's going to drive the database from application, no need to do any changes in your database when you have a schema changeEvery property in a document is getting indexed, no need to create indexes manually. Hash index is created for every path in the document, range based index is getting created for numbers & strings. You can define exclusion paths from a portion of your document you are never going to query, so you can save the unnecessary write time of the index. Indexing policies can be changed as application grows.
Go to Azure Cosmos DB account and click on Settings, then navigate to indexing policies for a one collection. In indexing policies, it has defined included paths & excluded paths arrays. By default it has added range index for numbers and strings. If you want to exclude some paths in your document, you can add it in excludedpaths array in this json document
9 Request Units (RU) & Pricing
Request Units are the currency in Azure Cosmos DB, each query has its own request charge, how much cost involved to process that requestRequest units are calculated based on the computation need to server the request, you can change your data structure by looking at the required request units
At first, design the database structure with collections & documents, if it requires many no of request units to process your queries, move your data into different collection or else remap your relationships differently
As application grows and access pattern of your users get changed, increase or decrease throughput in Cosmos DB service
When you create a collection you define the request units, RU is getting charged for stored procedures and triggers in your collection. If you go above that you start to getting throttled, we can define an alert to notify before getting throttled
Capacity units in Cosmos DB service measured in storage and throughput, we can select a capacity unit when creating the database and scale it later
10 Azure Document API
In Azure Document API, Document is a JSON object, it stores data as documents
Azure document has a flexible schema, de-normalized data, it can have mixed type of data such as a string value, number, array or an object
In Azure document API, referential integrity is not enforced as a relational database
11 How to model data for a document database
Modeling data in a document database is equally important as a relational database. It's slightly different than a relational data model.At first, model your data and run your queries, see what will be the cost for your queries, It it's expensive remodel your data until it comes to a certain level. When your application grows with data, you may want to restructure your data again
In a document database, schema enforcement needs to handle by the developers
12 Are you Non-relational ?
If we store product information in a relational database, you have a normalized data in different tables. When we want to show catalog, you should perform joins and convert that models to a view model. conversion from model to view model is going to handle by a ORM - (Object relational mapping)
When we store product catalog in a document database, you dont want to convert database model to something else to show it on the screen. What you store in the database is what we show on the screen
12.1 Modeling data in a relational way
We have mapped order in 4 different tables, when you want to show an order, you have to join all these tables and construct the order
12.2 Modeling data in document way
13 Embed or Reference
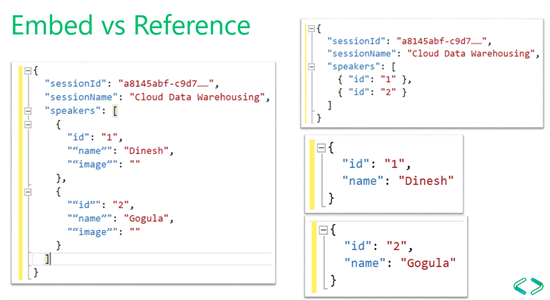
In above example, it shows a speaker session management system. For a speaker session it has sessionId & sessionName scalar properties.
In the left side it shows an example of an embedded relationship, speakers has been embedded into the speaker session document
If you want to show a speaker session on the screen, you have to read only one document, no need to join multiple documents
If you refer to the right side example, you have speakers in separate documents and session in another document, basically you have two type of documents, session type document and speaker type document
In speaker document, you have speaker id & name, In session document, speakers has been referenced by their ids
When we want to show speaker session details on the page, you have to join speaker document with session document
When you create entities in a document database, you can choose whether to go with an embedded or referenced relationship, according to the requirement you can select a relationship and create your documents & collections
14 Demo : How to design a order processing database
Let's create a Azure Cosmos DB account and create multiple collections and documents in it.
14.1 Create Cosmos DB account and collections
Create a Cosmos DB account to store order information, inside that create multiple collections to store orders, users and product comments. I will explain why we created separate collections for user and products
14.2 Explore collection & documents
14.3 Go through Order documents
Click on first document, it has order information along with customer details and items
Order document has customer information with order item details, since order processing system usually query an order, so no need to have multiple document for a customer and order items. We can store order items with customer, without any joins between documents, you can retrieve an order with a single read
In Order document, Customer object is embedded into an order, since Order & Customer get queried together
Order Items are stored as an array, For each order item a product has been embedded with product vendor information. In a document you can navigate to any level of property and retrieve information as application requires
If you see Order collection, you can store documents as well as can write a stored procedure, user defined function, trigger for a collection.
14.4 Let's check ProductComment collection
In ProductComment collection, we have stored comments for each product, As you remember we stored product information along with order and order item. But we have created separate collection for product comments
A product can have many no of comments from different users, if we store product comments along with product details that document can be very big in size. that's why its better to separate it to another document and store product comments as a bulk document that grows fast
If you see the structure of this document it has product id field, and product id field has been referenced in order document. Product and product comment entities has referenced relationship
14.5 Stored procedure in a collection
In a document database, data reads are faster but when it comes to data writes, it's going to be bit slower. so what we can do is we can run a stored procedure in the background to update necessary records
14.6 Why separate collection for Users
In this example, we created separate collection for Orders and another collection for users of the system.
User information is not getting queried with orders, that's why its better to have separate collections.
User document has his profile information and social media details as above. When we want to get user information you can read this user collection and retrieve all the necessary user details in a one single read
15 Let's query the document collection
Go to Order collection and click on New SQL Query, Let's get all the orders in Order collection. execute your query, It shows 2.65 RU as request charge. Order collection has 2 Order documents
Let's try to get a complete order by passing order id as above, It costs 2.31 request units (In previous query to retrieve 2 orders, it costs 2.65 request units)
You can use SQL syntax to run queries against document db collections
In previous queries, we projected Order entity. In above query we have started to query from order and projects order items. In where clause you can navigate to any property and filter from necessary information
If you can see the request charge for above query, its 2.58 request units, with the where clause request charge was bit high than this
This query returns all the customers lives in Colombo or Malabe, We have used IN operator in above query,
16 How we can use joins in document collection
You can see order document as above, we want to find item No 'AA1', We should navigate to Items array to reach Item No property, since Items is an array we have to perform a join, If we want to reach Customer address property, we can navigate from Order.Customer.Address since customer is an object
If we want to navigate to an array and perform some selection in a document collection, we should perform a join operation as above
Order collection joined with Order items then filtered from item no and projects order and item information
You can perform a range operation as above. It's the same query as above but with a different where clause
We want to get order and item information where itemNo is 'AA1' and vendor code is 'ABC'
At first, navigate to Order collection, (FROM o),
We should filter from item No, so navigate to Items, Items is an array, (JOIN Orders with Items array)
Then we should filter from vendor code, You can find Vendors array in each Product, (JOIN Vendors array with item)
You have performed two joins in this query, then you can filter the result in where clause and retrieve necessary information in select clause
You can run this type of a query and format its results as above
17 Conclusion
If the query charges are high, then you may have to restructure your collections, some referenced relationships may need to convert into embedded ones
If you documents are big in size, you may have to convert embedded relationship into a referenced relationship to maintain the cost for you data

























No comments:
Post a Comment